Welcome to the Programming Terms Glossary!

Welcome to the Programming Terms Glossary
On this page, you’ll find translations and explanations of various programming-related terms and concepts. Whether you’re new to the world of IT or looking to expand your knowledge, this glossary will help you better understand essential programming terms. Each term is clearly explained in simple language, providing a concise overview of technical concepts.
Who is This Glossary For?
This glossary is designed for students, professionals, and anyone interested in learning more about programming. It covers a wide range of terms from basic concepts like “variables“ and “functions“ to more advanced topics like “object-oriented programming“ and “algorithms“. Whether you’re just starting or already have experience, you’ll find this resource helpful for clarifying terms you might encounter in your studies or work.
Why Understanding Programming Terms is Important
Understanding the key terminology in programming is crucial for effective communication within the IT field. Programming languages, concepts, and methodologies often come with specialized terms that might seem confusing at first. With the help of this glossary, you’ll be able to navigate technical discussions more easily and enhance your ability to read and write code efficiently.
What You’ll Find in This Glossary
- Clear and concise definitions of programming terms
- Practical examples to illustrate the use of each term
- Translations of key concepts into understandable language for non-native speakers or beginners
How to Use This Glossary
To get the most out of this glossary, start by browsing the terms that are most relevant to you. If you’re working on a specific project or studying a particular programming language, look up the terms related to your current work. Each term is linked to its detailed explanation, so you can easily navigate between the definitions. For example, you can check out our pages on “JavaScript“ and “Python“ for specific programming language terms.
| 1.English | Definition | Russian |
| 2.Source code editor | Text editor program designed specifically for editing source code of computer programs. | Редактор исходного кода |
| 3.Programm | A series of operations that cintrol the function of a computer | Программа |
| 4.Programming language | Codes used to write commands to a computer | Язык программирования |
| 5.Programming software | Any software that supports the development of new applications | Программное обеспечение для программирования |
| 6.Interpreter | A computer program that changes the instructions in another program into a form that can be easily utderstood by a computer | Интерпритатор |
| 7.Complier | A computer program that changes instructions into machine language | Компилятор |
| 8.code | Intsructions that make up a program | Код |
| 9.an application ( app ) | One or several programs working together for the end user | Приложение |
| 10.a script | Instructions in a programming language that need to be interpreted | Скрипт |
| 11.Data Managment | the ability to track and evaluate information | Данные |
| 12.Satellite Navigation | the process of determining a location based on electronic information | Спутниковая навигация |
| 13.Payroll | a company’s list employees and how much they are paid | Расчет заработной платы |
| 14.Multimedia player | a device that can play audio, video and other files | Мультимедийный проигрыватель |
| 15.Digital assistant | a small, handheld computer that typycally works as a mobile phone | Цифровой помощник |
| 16.Bioinformatis | the application of computer software to the field of biology | биоинформация |
| 17.Threat | if the source of the damaging instructions is an individual who intended that the abnormal behavior occur, we call the instructions malicious code | Угроза |
| 18.firewall (brandmawer) | firewall permits access only to athorized users. It will deny access to anyone without proper credentials. | Сетевой экран |
| 19.Malware | any type of code that causes harm to a computer system or network | Вредоносная программа |
| 20.Antivirus Software | Don’t let uauthorized parties stal your personal information with spyware And stop viruses before they destroy your computer. The SharpAlert Exviro package protects against all types of malware. It quarantines infected files. Then threat removal just takes one click. | Защитная программа от вирусов |
| 21.Simulation | A realistic representation of something | Симуляция |
| 22.Security Software | The engineer installed a program that protects a computer foro various threats on he company’s systems | Защитная программа |
| 23.Spyware | Spyware steals and sends user data without consent. | Шпионская программа |
| 24.Removal | “Removal” means taking something away or eliminating it. | Удаление |
| 25.Quarantine | “Quarantine” means isolating to prevent harm. | Карантин |
| 26.Virus | “Virus” is harmful software. | Вирус |
| 27.IDE(Integrated Development Environment) | Software application that helps programmers develop software code effciently | Интегрированная среда разработки |
| 28.customize | “Customize” means personalizing or tailoring. | настроить |
| 29.arrange | orders the rows of a data frame by the values of selected columns. | организовать |
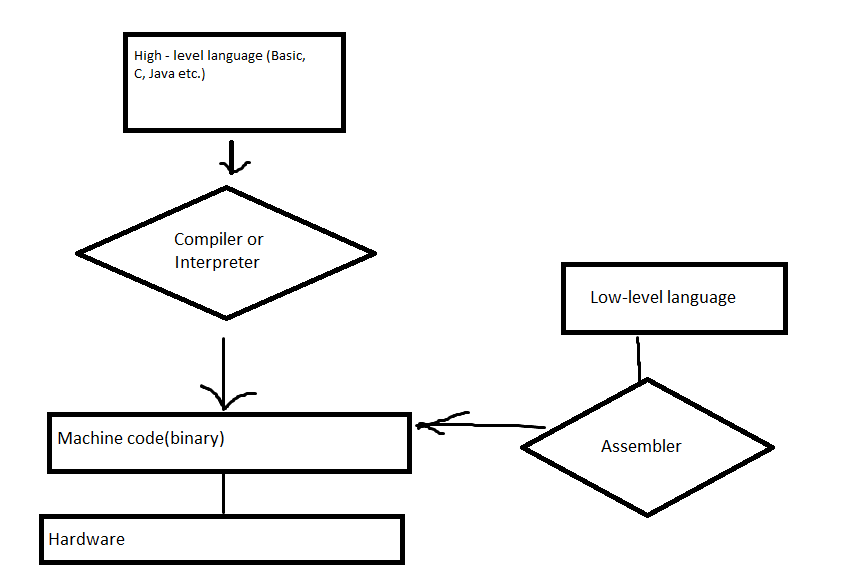
| 30.machine code | bainary code | машинный код |
| 31.assembly laungages | An assembler is a translator of a program from text in assembly language into a program in machine language. | языки ассемблера |
| 32.low level languages | “Low-level languages” are close to machine code. | языки низкого уровня |
| 33.high level languages | “High-level languages” are user-friendly and abstracted from machine code. | языки высокого уровня |
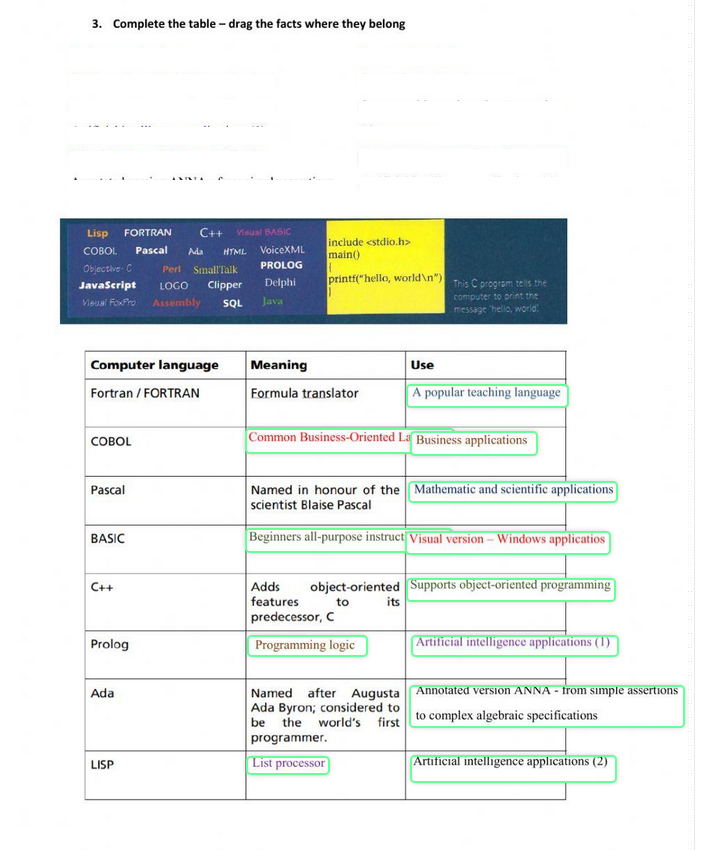
| 34. FORTRAN | FORTRAN is a programming language for math and science. | FORTRAN |
| 35.code editors | In programming, code editors are tools used to write, edit, and manage source code for software development. | кодовые редакторы |
| 36.script mode | Script mode in programming means executing code interactively, entering and executing commands one at a time. | скриптовый режим |
| 37.interactive mode | Interactive mode in programming allows users to enter commands or code directly into the interpreter or runtime environment, receiving immediate feedback or results. | интерактивный режим |
| 38.statements | Statements in programming are individual instructions or commands that perform a specific action or operation within a program. | привила |
| 39.objects | Objects in programming are instances of classes that encapsulate data and behavior, enabling modular and reusable code. | обьекты |
| 40.classes | Classes in programming are templates for creating objects, defining their attributes and behaviors. | классы |
| 41.variables | переменные | |
| 42.GUI | графический интерфейс пользователя | |
| 43.CLI | интерфейс командой строки | |
| 44.the shell | оболочка | |
| 45.machine code | The only language computers can undestand directly is machine code. | машинный код |
| 46.object oriendted programming | The programmer concevtrataes on paricular things and gives each object functions which can be altered without changing the entire programm. | Обьектно орентированное програмирование |
| 47.object code | it convents the entire program into machine code in one go on the order hand, an interpreter translates the source code line by line as the program is running. | |
| 48.markup languages | to format and link text files | |
| 49.HTML | Hyper Text Marking Language | |
| 50.XML | Extensible Markup Language | |
| 51.VoiceXML | VoiceXML is used to create voice applications that run on the phone where as HTML is used to create visual applications | |
| 52.COBOL | Common Bussines Orieneted Language | |
| 53.Flowchart | A diagram represanting the successive logical steps | блок схема |
| 54. source code | Program instruactions written in a particular computer language | |
| 55.compiler | A special program hich converts the source program into machine code –the noly language unrstood by the processor. | |
| 56.debugging | The techniques of detecting and correcting errors (or bugs) which may occur in programs. | |
| 57.text coding | Text-based programming involves typing lines of code that tell computers what task to perform. It involves writing words, phrases, numbers and symbols in a certain order, so it makes sense to the computer — just like spelling and grammar in any other language | |
| 58.tenserflow | TensorFlow is defined as an open-source platform and framework for machine learning, which includes libraries and tools based on Python and Java — designed with the objective of training machine learning and deep learning models on data | |
| 59.terminal | A terminal is simply a text-based interface to the computer. In a terminal, you can type commands, manipulate files, execute programs, and open documents. When working in a terminal, the current directory is called your working directory. A terminal will usually start in the top-level directory of your account. | |
| 60.plug-in | an auxliary program that enable web browser to support new content for example animation | |
| 61. applet | a small Java application usually designed to run automatically within a web page | |
| 62.Java | an island in Indonesian coffe in American slang and a programming language for internet applications | |
| 63. object oriented programming | a computer programming tchnique that allows the creationof objects that interact with each other and can be used as the foundation of others used to create graphical user interfaces | |
| 64. platform independement | software that can run on any operating system | |
| 65. Strings | Definition. A string is a data type used in programming, that is used to represent text rather than numbers. A string is a sequence of characters and can contain letters, numbers, symbols and even spaces. | |
| 66. Statements | In computer programming, a statement is a syntactic unit of an imperative programming language that expresses some action to be carried out. A program written in such a language is formed by a sequence of one or more statements. | |
| 67. Coding languages | A programming language is a set of instructions written by a programmer to deliver instructions to the computer to perform and accomplish a task. This set of instructions is usually viewed as incomprehensible code structured following a definite programming language syntax. | |
| 68. Arithmetics operators | An arithmetic operator is a mathematical function that takes two operands and performs a calculation on them. They are used in common arithmetic and most computer languages contain a set of such operators that can be used within equations to perform a number of types of sequential calculation. | |
| 69. Assignment operators | The assignment operator = assigns the value of its right-hand operand to a variable, a property, or an indexer element given by its left-hand operand. The result of an assignment expression is the value assigned to the left-hand operand | |
| 70. While loops | Loops, but this loop is breaking then when some condition statement will changed | Цикл |
| 71. For Loops | A «For» Loop is used to repeat a specific block of code a known number of times. For example, if we want to check the grade of every student in the class, we loop from 1 to that number. When the number of times is not known before hand, we use a «While» loop. | |
| 72. Algorithm | An Algorithm is a step-by-step procedure or set of rules for solving a specific problem or performing a task. It provides a clear, structured approach to solving problems and is fundamental to coding and programming. Algorithms can be expressed in various forms, such as pseudocode or flowcharts, and implemented in different programming languages. | |
| 73. Data Structure | A Data Structure organizes and stores data in a computer’s memory or storage system. It defines the relationships, operations, and access methods for efficiently manipulating and retrieving data. Data structures include arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, and graphs. | |
| 74. Error Handling | Error Handling is anticipating, detecting, and handling errors or exceptions that may occur during program execution. It involves implementing strategies, such as try-catch blocks or error codes, to handle errors and prevent program crashes or unexpected behavior safely. | |
| 75. Function | A Function, a method, or a subroutine is a reusable block of code that performs a specific task or calculation. Functions help organize code, improve modularity, and enable code reuse. They accept input parameters, perform operations, and may return a value. | |
| 76. Git | Git is a distributed version control system widely used in software development. It allows multiple developers to collaborate on a project, track changes, and manage different code versions. Git enables efficient code management, facilitates collaboration, and provides conflict resolution mechanisms. | |
| 77. Loop | A Loop is a programming construct that allows repetitive execution of a code block based on a specified condition. It helps automate tasks and process large amounts of data efficiently. Common loops include the for loop, while loop, and do-while loop. | |
| 78. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) | Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that organizes code around objects, which are instances of classes. It emphasizes concepts such as encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. OOP allows modular and reusable code, promotes code organization, and facilitates software maintenance and extensibility | |
| 79. Refactoring | Refactoring is the process of restructuring and improving existing code without changing its external behavior. It involves making code modifications to enhance readability, maintainability, and performance while preserving its functionality. Refactoring helps eliminate code smells, improve code organization, and reduce technical debt | |
| 80. Stack | A Stack is a data structure that follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle in programming. It allows elements to be added or removed only from one end, the top. Stacks are commonly used for managing function calls, tracking program execution, and handling recursive algorithms. | |
| 81. Syntax | Syntax refers to the rules and conventions that dictate the structure and format of a programming language. It defines how instructions and statements are written to form valid and meaningful code. Following the correct syntax is essential for the compiler or interpreter to understand and execute the code accurately. | |
| 82. Web Development | Web Development encompasses the creation and maintenance of websites and web applications. It involves designing user interfaces, writing code, integrating databases, and implementing functionality using web technologies such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and server-side scripting languages. Web development focuses on creating engaging and interactive experiences for users on the web | |
| 83. Version Control | Version Control, also known as Source Code Management (SCM), tracks and manages source code file changes. It allows developers to collaborate, maintain different versions of code, and track modifications over time. Version control systems, such as Git or SVN, provide mechanisms for branching, merging, and reverting changes | |
| 84. Variable | A Variable is a named storage location in a computer’s memory that holds a value or data. Variables are used to store and manipulate data during program execution. They have a specific data type (integer, string, or boolean) and can be assigned new values throughout the program. | |
| 85. Performance Optimization | Performance Optimization refers to improving a software application’s speed, efficiency, and resource utilization. It involves analyzing and fine-tuning code, algorithms, and system configurations to minimize execution time, reduce memory usage, and optimize overall performance. Performance optimization aims to deliver a fast and responsive user experience | |
| 86. Back-end | The element of a computer system or programme that is normally in charge of storing and maintaining data but which the end user does not directly access or utilise is the back-end . The person in charge of creating back-end services is a back-end developer | |
| 87. Boolean | True / False | |
| 88. Branch | A branch in Git is a new version of the main repository that includes copies of all the documents and history at the time of separation without actually duplicating all the contents. This enables the subsequent merging of all changes made to the branch back into the main repository. | |
| 89. C++ | C++ is a simple but functional programming language. People who learn this language will be capable of comprehending complex instructions and understanding how programmes operate | |
| 90. Cache | To help with faster load times from repetitive activities, a cache is the temporary storage of data and information. Without caching, it would take some time for each user that calculates taxes to finish. However, with caching, only the initial user would need to conduct the calculation; subsequent users who meet the same “tax criteria” would have access to the pre-calculated results and receive their results almost immediately. | |
| 91. Char | One alphabetic symbol is equal to one display unit of data called a “char character”. A char variable’s value could be any single character, including “a,” “1,” “$,” and “X.” This definition of character is predicated on the common understanding of a character as a single literary element. In contrast, the abbreviation char is a conserved keyword in the programming languages C, C++, C#, and Java. | |
| 92. CSS | CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets. It is what adds style and colour to every webpage. While HTML controls the structure of a document with paragraphs, headers and images, Cascading Style Sheets allow you to specify colours, fonts, layouts and more. | |
| 93. Database | A platform designed for data storage, organisation, and retrieval is called a database. | |
| CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) | The setting applied to a CSS property, defining aspects like color, size, position, etc. | |
The Table of Comprasion of Programming Languages
| Visual BASIC | Java | Python | Visual XML |
| Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code. | Java doesn stand for anything | Python is an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language with dynamic semantics developed by Guido van Rossum. It was originally released in 1991. Designed to be easy as well as fun, the name «Python» is a nod to the British comedy group Monty Python. | XML stands for eXtensible Markup Language. |
| was first develepoed by Microsoft in 1991 | Java was developed by James Gosling in 1996 on January 23 | 20 February 1991 | Was developed in the late 1990s |
| VB is a GUI-based development tool that offers a faster RAD than most other programming languages. VB also features syntax that is more straightforward than other languages, a visual environment that is easy to understand and high database connectivity. | Java main features include platform independece and object-orinted programming | Python is a high-level programming language. Python is very easy to learn the language as compared to other languages like C, C#, Javascript, Java, etc. It is very easy to code in the Python language and anybody can learn Python basics in a few hours or days. It is also a developer-friendly language. | Graphical representantion Drag and drop functionality Syntax highlighting and validation |
| Visual Basic is written in Visual Studio and can be used to create executable files that can run independently. | Java is used for applications or web sites | Build websites and software, automate tasks, and conduct data analysis. | XML document creation Data modeling Prototyping |
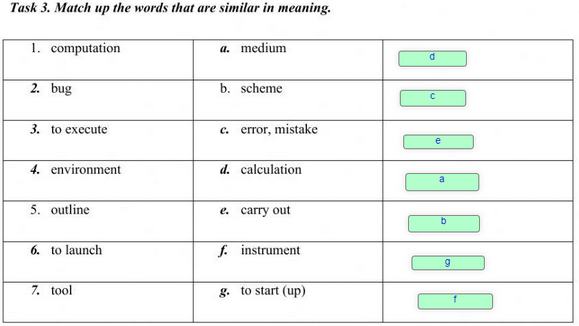
Termins explaining
Iseseisev töö





Computer Programming
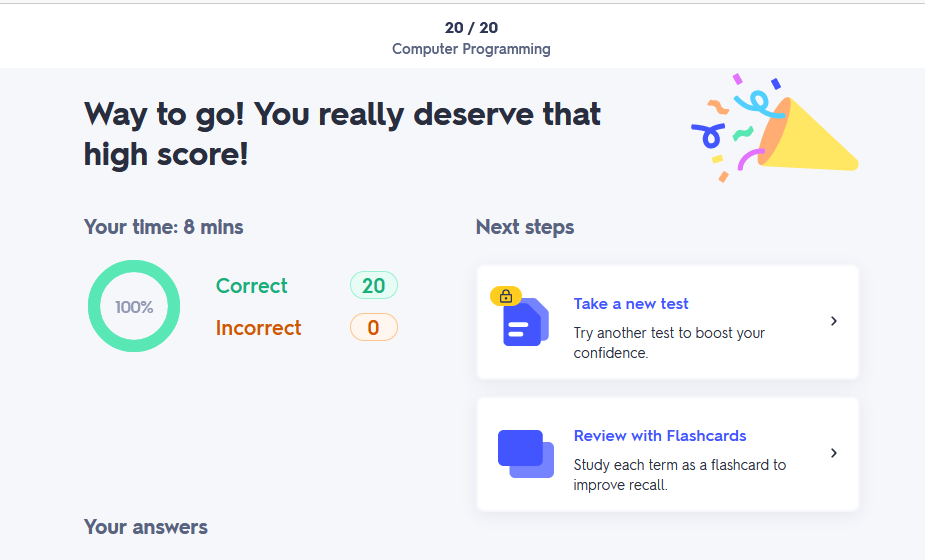
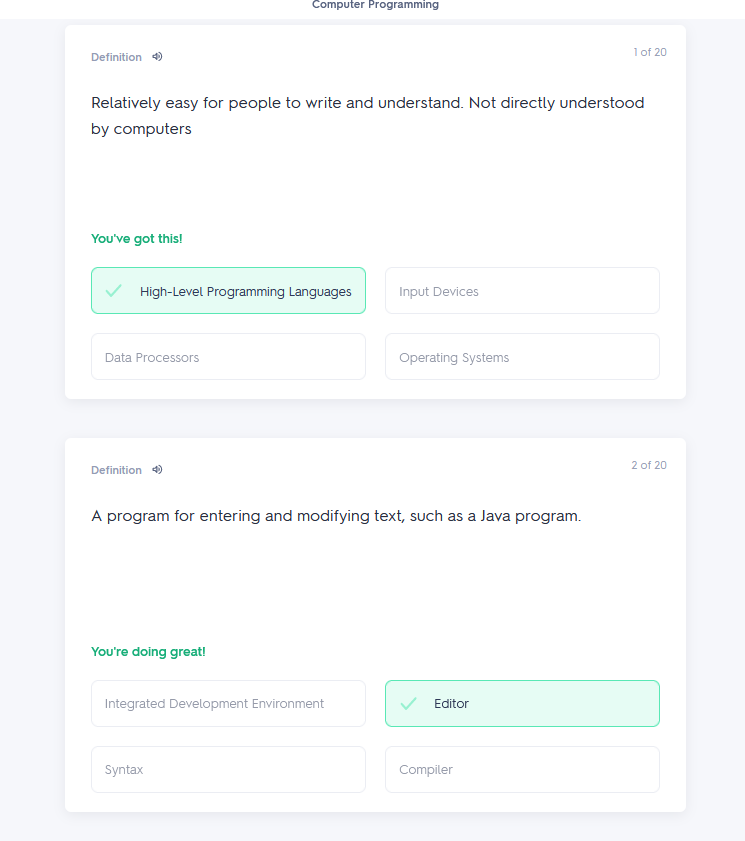
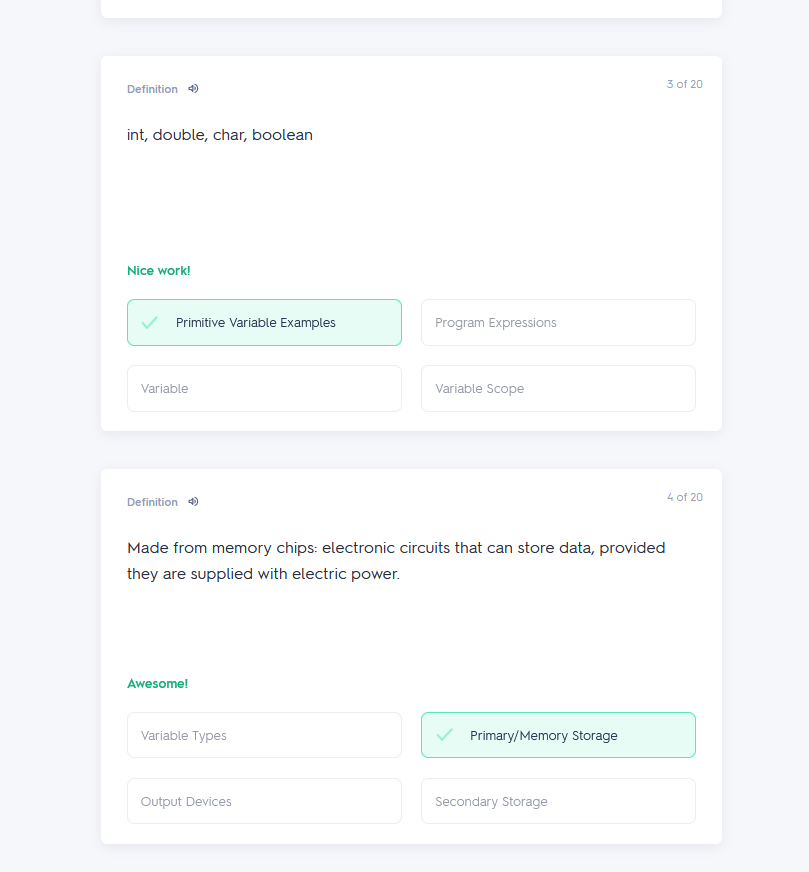
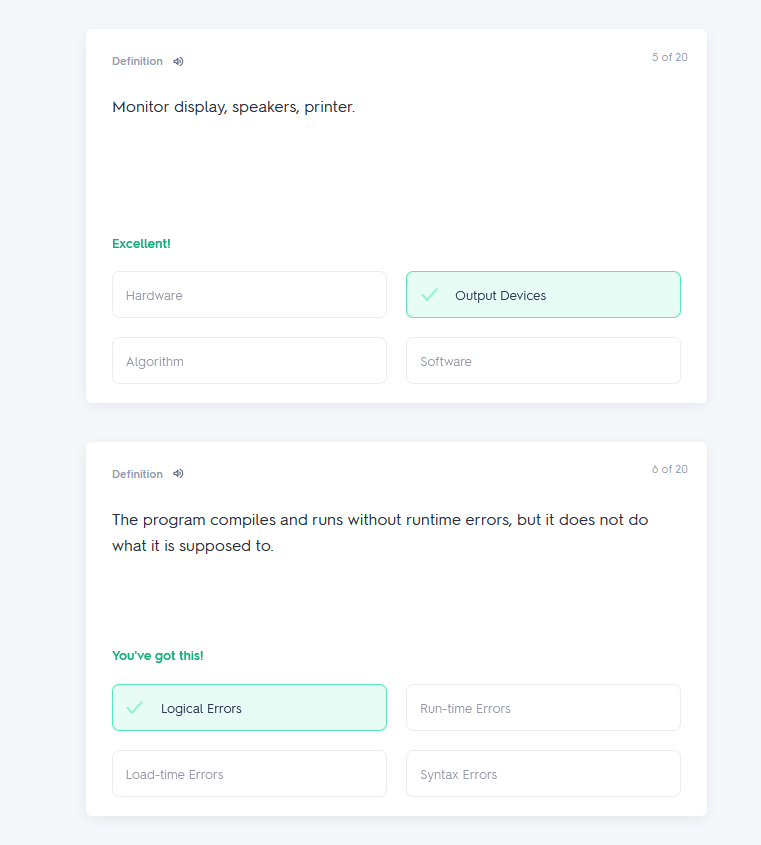
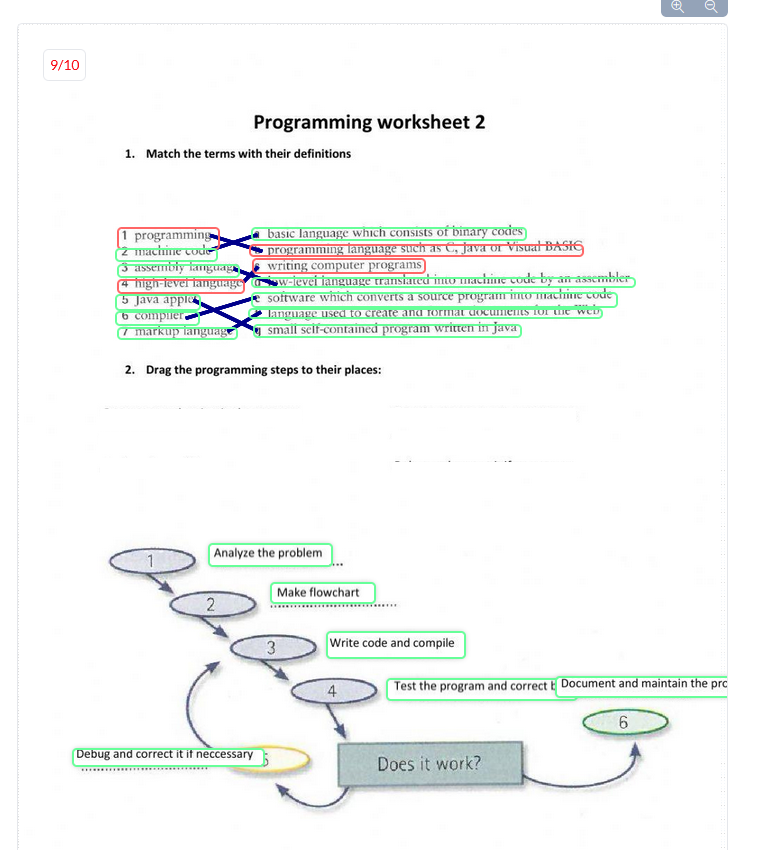
Programming worksheet 2

The Java Language
A#
1. Java was invented by Sun Microsystem
2. With theinterpreter a program is translated into Java bytecode.
3. Java is compatible with most computing platforms
4. Java programs typically run in a multi-threaded manner, with more than one part executing at a time.
5. Java does have competitors in the programming language space.
6. Flash files are not called animations they are typically referred to as SWF files
B#
1 A
2 D
3 F
4 B
5 E
6 C
C#
1) animated
2) object-oriented
3) complied, interpreted
4) used
5) configured
6) pronounced
TEST
- Logo
2) C++
3) FORTRAN
4) HTML
5) Visual Basic
6) Ada
7) Cobol
8) MXL
9) Pascal
10) Logo
11) C++